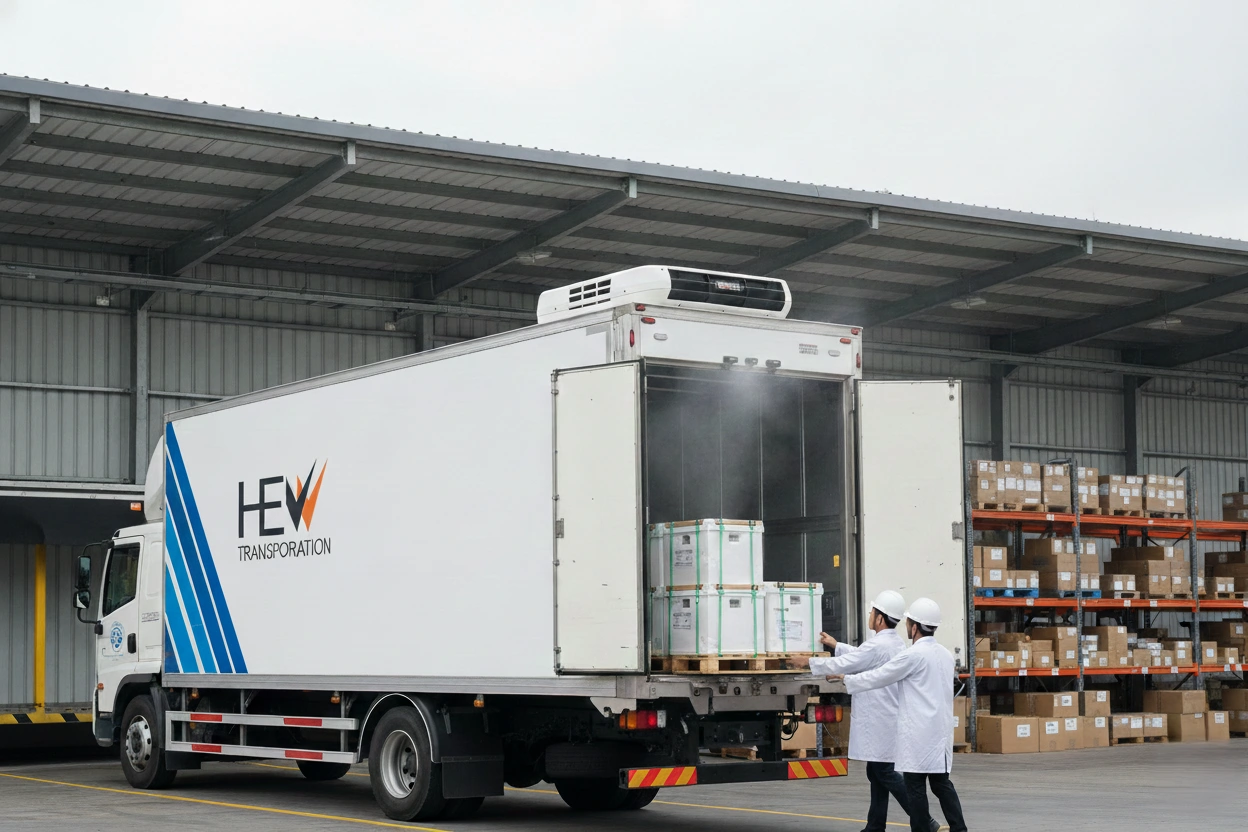
Overview of How Healthcare Uses Cold Chain Logistics
Cold chain logistics in healthcare refers to the temperature-controlled storage, handling, and transportation of medical items that are highly sensitive to heat, humidity, or light. These items include vaccines, pharmaceuticals, biologics, blood products, lab samples, and medical reagents, all of which can lose effectiveness if exposed to the wrong conditions for even a short period.
Healthcare systems rely on cold chain logistics to:
- Maintain product safety
- Prevent temperature excursions
- Ensure regulatory compliance
- Deliver medicines quickly to hospitals, clinics, and patients
- Keep national immunization programs stable
- Support emergency response and pandemic preparedness
Because these supplies directly affect patient health, cold chain management is considered one of the most critical pillars of modern medical logistics.
This guide explains how healthcare uses cold chain logistics, why it matters, and how specialized transport companies like us deliver reliability, precision, and compliance.
Why Cold Chain Logistics Is Essential in Healthcare
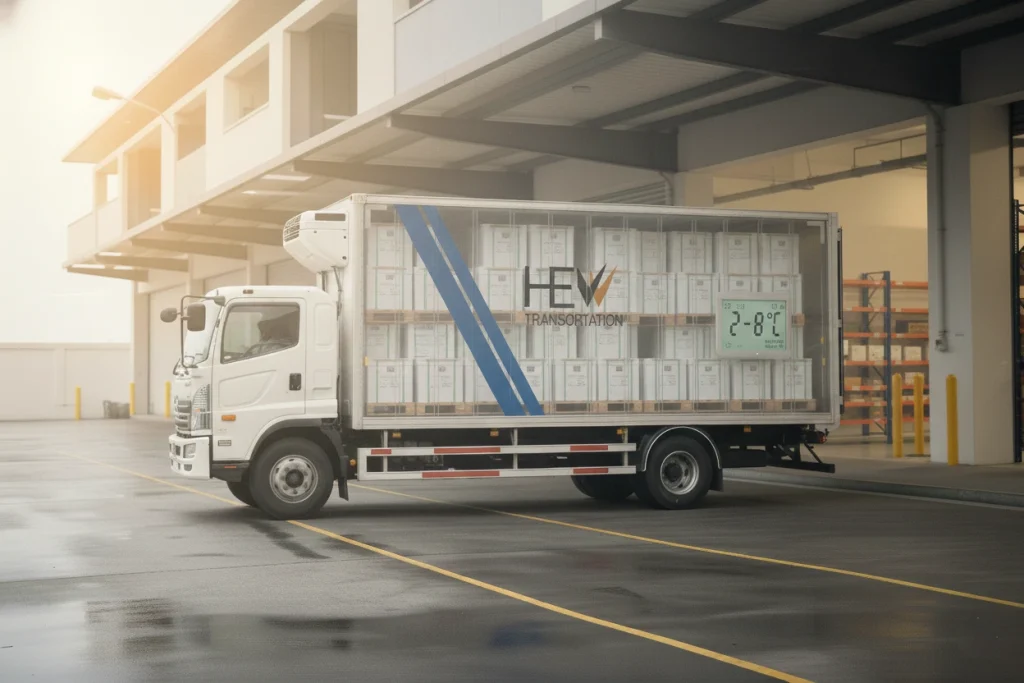

Without cold chain systems, the global medical ecosystem would collapse. Sensitive healthcare materials begin degrading quickly when exposed to fluctuating temperatures, compromising patient safety.
Healthcare uses cold chain logistics to protect:
- Vaccines (most require +2°C to +8°C)
- Biologics like insulin, monoclonal antibodies, and cell therapies
- Pharmaceuticals that require strict temperature ranges
- Blood and plasma stored between +1°C and +6°C
- Organs and tissues for transplant transported at controlled temperatures
- Diagnostic samples such as COVID swabs, blood samples, and DNA tests
- IV nutrition and chemotherapy drugs
Statistic: WHO reports that over 25% of vaccines globally are degraded due to improper cold chain handling, causing billions in losses and risking lives.
How Cold Chain Logistics Works in Healthcare
Healthcare cold chain operations follow a strict multistage cycle:
Storage Phase
Medical products are stored in:
- Pharmaceutical cold rooms
- Temperature-controlled warehouses
- Medical refrigerators and freezers
- Cryogenic freezers (–80°C or below)
Each facility is equipped with:
- IoT temperature sensors
- Backup power systems
- Automated alarms
- SOP-driven handling processes
Pre-Transport Conditioning
Before transport, staff ensure:
- Packaging is validated.
- Gel packs or dry ice are prepared.
- Insulated medical containers are sealed.
- Temperature data loggers are activated.
- Documentation and compliance labels are attached.
Transportation Phase
Depending on the medical item, healthcare uses different cold chain vehicles:
- Refrigerated vans
- Freezer vans
- Chiller trucks
- Multi-zone temperature vehicles
- Express medical couriers
Vehicles must maintain temperatures like:
| Medical Item | Required Temperature |
|---|---|
| Vaccines | +2°C to +8°C |
| Plasma | –30°C or below |
| Frozen reagents | –20°C |
| Biologics | +2°C to +8°C |
| COVID samples | +2°C to +8°C |
Cold chain transportation companies use:
- Real-time GPS
- Temperature tracking
- Door-open alerts
- Route optimization
- Compliance documentation (GDP, MOH, ISO standards)
Delivery Phase
Upon arrival:
- Staff verify temperature logs
- Packages are inspected
- Items are moved into controlled storage immediately
- Digital proof-of-delivery is sent to the client
This end-to-end system ensures healthcare products remain safe from origin to final use.
Where Healthcare Relies on Cold Chain Logistics
Cold chain logistics is used across hospitals, pharmaceutical companies, laboratories, and public health agencies.
Hospitals & Clinics
- Chemotherapy drugs
- ICU medicines
- Blood bags
- Emergency supplies
Pharmaceutical Manufacturers
- Vaccine distribution
- Clinical trial shipments
- Temperature-sensitive raw materials
Laboratories & Diagnostics
- COVID-19 samples
- DNA testing kits
- Microbiological cultures
Home Healthcare
- Home-delivered insulin
- Nutritional IV therapy
- Patient-specific biologics
Real-World Case Study (Based on Cold Chain Best Practices)
A national immunization program required transporting vaccines from central storage to clinics islandwide. The challenges included:
- Maintaining +2°C to +8°C throughout the trip
- Preventing temperature excursions in Singapore’s high heat
- Ensuring safe, same-day distribution
By using calibrated chiller vans, real-time temperature monitoring, validated insulated boxes, and strict loading procedures, the delivery success rate reached 99.8% compliance, ensuring safe administration across all clinics.
Learn More About Medical Cold Chain Systems
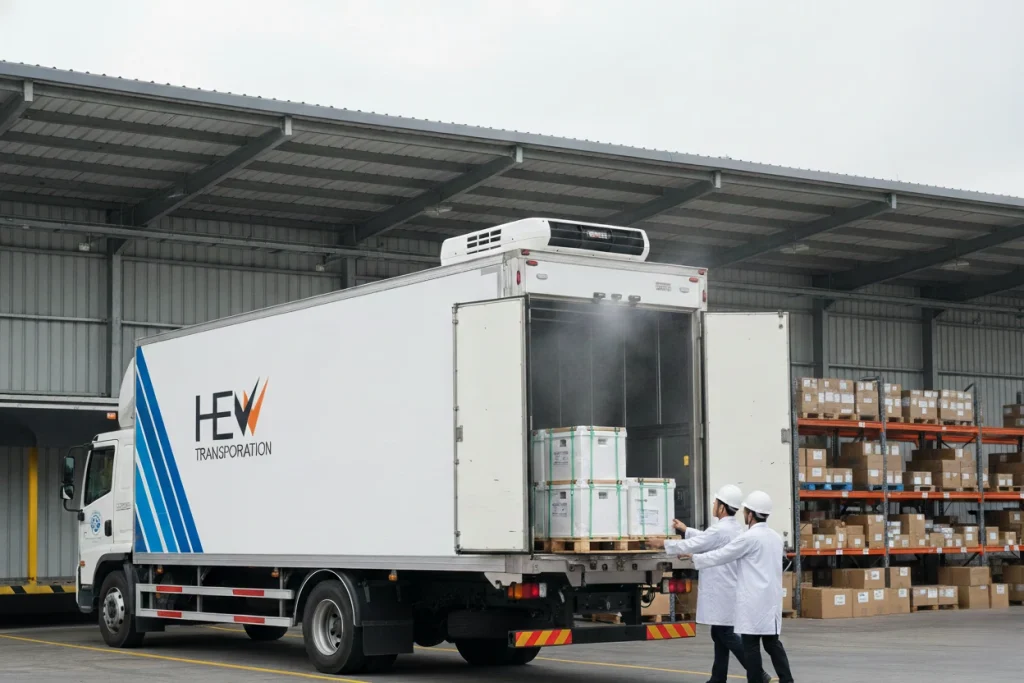

To understand the step-by-step process in more detail, see our guide: how medical cold chain transport works.
Conclusion: Why Healthcare Trusts Cold Chain Specialists Like Us
The healthcare sector depends on cold chain logistics to protect medicines, vaccines, samples, and life-saving supplies from temperature damage. Reliable cold chain transportation isn’t optional, it directly protects patient safety and national health systems.
As a professional cold chain logistics provider, we ensure:
- Precise temperature control
- Safe and compliant medical transport
- Real-time monitoring
- Fast, reliable delivery
- Expertise in pharmaceutical and healthcare handling
For organizations seeking dependable medical cold chain transport, visit our website to explore how our specialized solutions support healthcare operations in Singapore.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Why is cold chain important for vaccines?
Vaccines lose potency if exposed to temperature swings. Cold chain prevents this degradation.
Can medicines be transported with normal couriers?
No. Medical items require validated vehicles, trained handlers, and regulatory compliance.
What happens if a temperature excursion occurs?
The product may be quarantined, tested for viability, or discarded based on SOPs.
Do all medicines need refrigeration?
Not all, but biologics, insulin, vaccines, and many antibiotics do.
How do hospitals track cold chain deliveries?
Using real-time trackers, digital logs, and certified temperature data loggers.