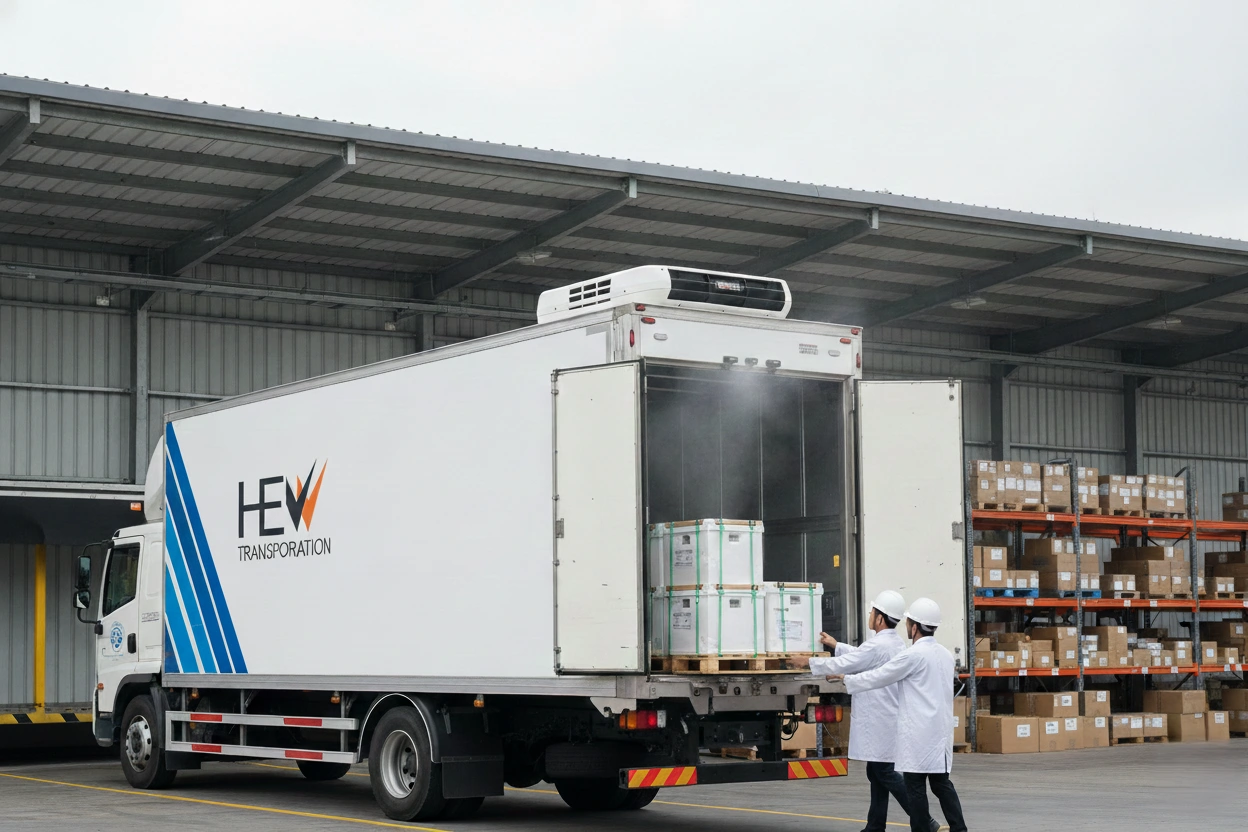
Cold chain best practices for restaurants refer to the standardized workflows, technologies, and handling procedures used to preserve the quality, freshness, and safety of temperature-sensitive food items from storage to preparation and delivery. For restaurants, this process is critical because improper temperature control can lead to bacterial growth, foodborne illnesses, spoilage, and major operational losses.
As a team specializing in temperature-controlled logistics and cold chain management, we understand how essential it is for restaurants to implement consistent, reliable, and compliant cold chain procedures. This guide outlines the most effective strategies, recommended tools, operational workflows, and quality control processes that help restaurants maintain safe temperatures at every stage of their operations.
Understanding Cold Chain Best Practices for Restaurants

Restaurants handle a wide variety of perishable foods, including meats, seafood, dairy, sauces, frozen goods, vegetables, and ready-to-eat items. Because these food types have different temperature requirements, maintaining a proper cold chain is not optional; it is a core requirement for safe food service.
Below is a simplified overview of the lifecycle of cold food within a restaurant:
- Receiving: Verify supplier temperatures and product condition.
- Storage: Maintain stable refrigeration and freezing temperatures.
- Preparation: Follow strict thawing, holding, and cross-contamination rules.
- Transport/Delivery: Use insulated packaging and temperature-controlled vehicles.
- Monitoring: Record temperatures throughout each stage.
Restaurants that lack structured cold chain practices often face issues such as premature spoilage, failed inspections, increased food waste, and customer safety risks.
Essential Temperature Standards for Restaurant Cold Chain Operations
To maintain food safety, restaurants should follow global standards such as FDA, WHO, and local food safety authority requirements.
Here is a summary of commonly accepted temperature ranges:
| Food Category | Optimal Temperature |
|---|---|
| Frozen meats, seafood, desserts | -18°C or lower |
| Chilled dairy, fresh meat | 0°C to 4°C |
| Fresh vegetables & fruits | 1°C to 5°C |
| Cooked or ready-to-eat foods (cold holding) | 1°C to 4°C |
| Hot foods (not cold chain but relevant) | 60°C or higher |
Maintaining these temperatures at every stage reduces microbial growth and keeps food fresh for longer.
Implementing Best Practices in Restaurant Cold Chain Workflows
Proper Receiving and Inspection Procedures
When suppliers deliver food, the receiving step becomes the first critical control point. To strengthen the cold chain:
- Measure and record product temperatures immediately upon arrival.
- Reject any items with damaged packaging, unusual odor, or temperature deviations.
- Load items into storage without delay.
Optimizing Cold Storage Management
Restaurants should maintain organized, well-maintained refrigeration zones. Best practices include:
- Separating raw and cooked products to prevent cross-contamination.
- Using FIFO (First In, First Out) rotation.
- Avoiding overstocking that restricts airflow.
- Installing temperature alarms for early detection of refrigerator failures.
Safe Thawing and Preparation Techniques
Thawing is often where restaurants make mistakes. The safest methods include:
- Thawing inside a refrigerator (never at room temperature).
- Using cold running water for sealed items.
- Keeping foods at 4°C or below during preparation.
- Minimizing the time foods spend outside the cold zone.
Packaging and Delivery: Ensuring Temperature Stability During Transit
Restaurants offering food delivery must ensure products maintain cold temperatures until they reach the customer.
Best practices:
- Use insulated delivery bags or boxes with gel packs.
- For larger volumes, use refrigerated vans.
- Add temperature indicators for safety verification.
- Train delivery teams on proper handling procedures.
For more detailed packaging strategies, you may refer to our internal guide using the anchor: technology used in cold chain logistics.
Recommended Tools and Technologies for Restaurant Cold Chain Management
Modern cold chain management relies heavily on automation, monitoring, and digital tracking. Some tools restaurants can use include:
1. IoT Temperature Sensors: Real-time temperature monitoring with automated alerts.
2. RFID Tags: Trace food movement from receiving to kitchen.
3. Smart Refrigeration Units: Energy-efficient refrigerators with built-in alarms and data logging.
4. Digital Inventory and Quality Control Software: Helps track batch numbers, expiry dates, and storage conditions.
5. Infrared Thermometers and Probe Thermometers: Fast and accurate on-spot temperature checks.
Using these technologies strengthens compliance and reduces risks dramatically.
Case Study: How Restaurants Improve Performance with Cold Chain Best Practices

A mid-sized catering company in Singapore implemented structured cold chain procedures in combination with real-time monitoring devices. Within six months, they achieved:
- 42% reduction in food waste
- 100% compliance during surprise safety inspections
- 60% fewer customer complaints about food condition during delivery
This real-world example shows that adopting structured cold chain systems improves business outcomes significantly.
Conclusion: Strengthening Restaurant Operations Through Reliable Cold Chain Management
Restaurant safety, customer satisfaction, and regulatory compliance depend heavily on maintaining a reliable and consistent cold chain system. With structured procedures, continuous monitoring, and modern technologies, restaurants can protect product quality from supplier delivery to dine-in service.
If your restaurant needs professional support in maintaining safe cold chain workflows, temperature-controlled delivery, or operational improvements, you can explore our full range of specialized services on our website HEW Transportation.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Why do restaurants need strict cold chain procedures?
Because temperature-sensitive foods spoil quickly and can cause foodborne illnesses if improperly stored or transported.
What technology helps restaurants maintain the cold chain?
IoT sensors, refrigerated vehicles, insulated packaging, and digital tracking systems.
Can food be safely thawed at room temperature?
No. Room-temperature thawing encourages rapid bacterial growth.
What is the ideal temperature for chilled food storage?
Typically between 0°C and 4°C depending on the product.
How do restaurants keep delivery items cold?
By using insulated packaging, cooling elements, and temperature-controlled transportation.