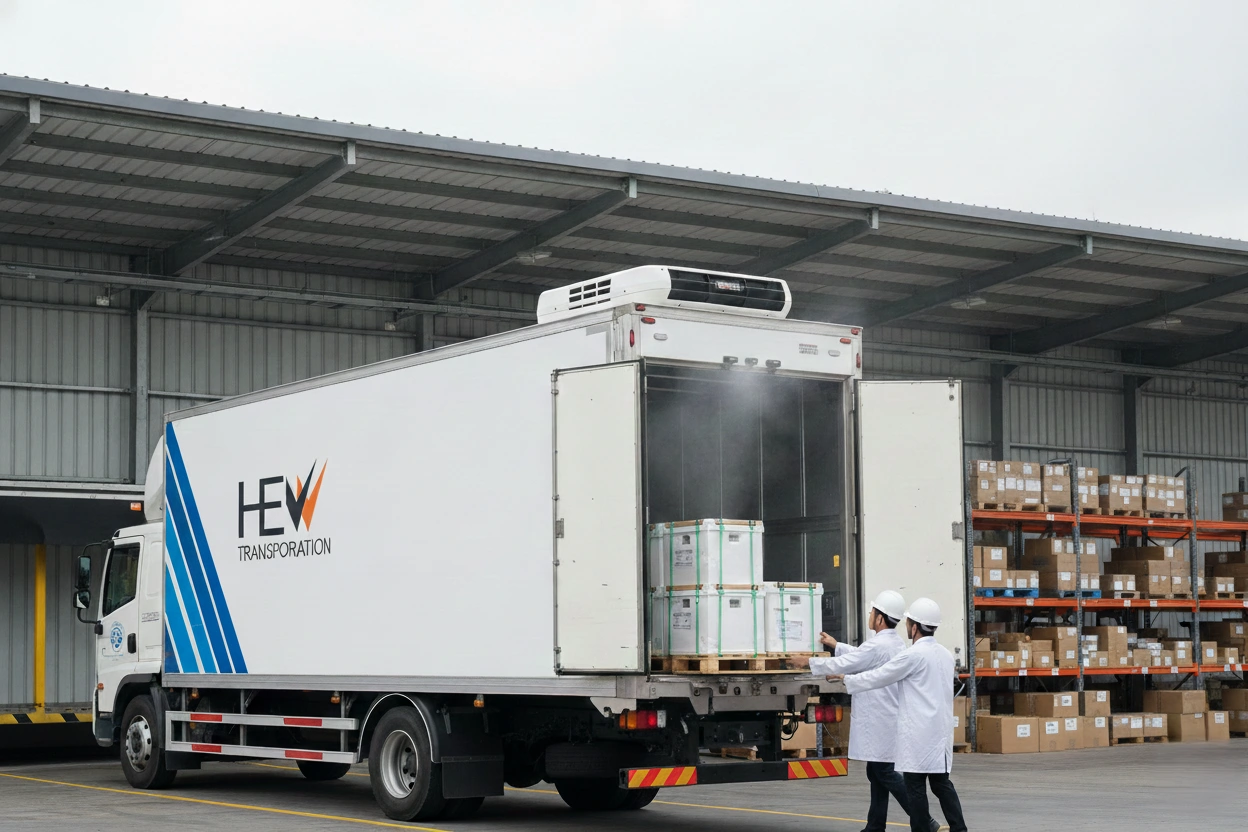
Cold chain delivery works as a highly controlled logistics process designed to maintain specific temperature ranges from the moment a product is prepared to the point it reaches customers, retailers, or healthcare facilities. This system ensures sensitive goods, such as frozen foods, fresh produce, pharmaceutical products, vaccines, and specialty chemicals, remain safe, stable, and compliant with strict regulatory standards. Because any small temperature deviation can cause spoilage or quality loss, a reliable cold chain solution requires precise coordination, real-time monitoring, and specialized equipment.
As a team dedicated to temperature-controlled transport and operational excellence, we focus on creating end-to-end cold chain workflows that protect product quality at every stage. This comprehensive guide explains how cold chain delivery works, the stages involved, the equipment used, common challenges, and best practices organizations should adopt. For businesses interested in packaging optimization, our in-depth guide on packaging tips for cold food delivery covers insulation techniques, coolant usage, and labeling standards to further support cold chain operations.
Understanding the Cold Chain System
Overview of Temperature-Controlled Logistics
Cold chain delivery operates through a structured system consisting of controlled environments, specialized vehicles, insulating materials, IoT monitoring tools, and standardized handling protocols. Every movement in the supply chain, from warehouse storage to the loading dock, transportation, and final delivery, must prevent temperature fluctuations.
Key Temperature Categories
Different goods require different thermal conditions:
| Product Type | Ideal Temperature Range | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Frozen food | –18°C or below | Must remain fully frozen |
| Chilled food | 0°C to 4°C | Fresh produce, dairy, ready-to-eat meals |
| Pharmaceuticals | 2°C to 8°C | Vaccines and biotech products |
| Ice cream | –20°C to –25°C | Highly sensitive to melting |
| Specialty chemicals | Varies | Dependent on chemical stability |
Core Process: How Cold Chain Delivery Works
1. Pre-Cooling and Product Preparation
Before goods enter the delivery pipeline, they must be cooled to their required temperatures using blast chillers, flash freezers, or specialized conditioning rooms. Pre-cooling prevents heat from being transferred into transportation containers.
Key activities include:
- Bringing products to target temperature
- Sorting and packaging based on category
- Applying labels for temperature requirements
- Checking compliance based on industry regulations
2. Cold Storage
Once prepared, goods are placed in chilled or frozen warehouses with automated climate control systems.
Storage technologies may include:
- Walk-in freezers
- Constant-temperature cold rooms
- Humidity-controlled environments
- RFID and barcode-tracking systems
Maintaining stable temperatures prevents microbial growth, oxidation, and biochemical degradation.
3. Loading and Transfer Protocol
Heat exposure during loading is one of the biggest risks in cold chain delivery. That is why professional teams follow strict SOPs such as:
- Minimizing door-open time
- Organizing pallets and crates in advance
- Using loading bay temperature curtains
- Conducting quick placement into refrigerated vehicles
Technology Used in Cold Chain Delivery
Cooling Tools and Insulation Materials
Cold chain delivery relies on engineering-grade insulation and cooling elements such as:
- Polyurethane foam insulated boxes
- Gel packs
- Dry ice
- Phase change materials (PCMs)
- Vacuum-insulated panels (VIP)
Real-Time Temperature Monitoring
IoT devices track temperatures across all delivery stages.
Common tools include:
- GPS sensors
- Humidity trackers
- Data loggers
- Cloud-based analytics dashboards
These systems alert teams instantly if temperatures deviate from safe thresholds.
Refrigerated Vehicles
Refrigerated vans, reefer trucks, and multi-temperature vehicles maintain stable thermal conditions throughout transit. These vehicles feature:
- Compressor-based refrigeration
- Insulated compartments
- Backup power systems
- Temperature zoning (for transporting mixed goods)
Last-Mile Execution in Cold Chain Delivery
Delivery Process
The final delivery stage requires precision because it is the moment where most temperature breaches occur.
Steps include:
- Confirming the recipient location
- Ensuring the vehicle temperature remains stable
- Using insulated bags or portable coolers for short transfers
- Capturing delivery evidence and documentation
- Providing temperature logs when required
Challenges During Last Mile
- Traffic delays
- Weather exposure
- Long delivery windows
- Inadequate recipient preparation
Reliable teams anticipate these risks with contingency planning.
Common Challenges and How We Solve Them
Cold chain operations face multiple challenges that can compromise product integrity. Here is how our systems address them:
| Challenge | Solution |
|---|---|
| Temperature fluctuations | Continuous IoT monitoring + alert systems |
| Long loading times | Pre-staged packaging + rapid loading SOP |
| Equipment failure | Backup refrigeration + preventive maintenance |
| Human error | Training and standardized workflow procedures |
| Delays | Optimized routing + contingency planning |

Conclusion and Next Steps
Cold chain delivery works by integrating temperature control, insulated packaging, refrigeration technology, and real-time monitoring into a seamless logistics system. Every stage, from pre-cooling to last-mile execution,must remain consistent to protect product quality and meet customer expectations.
If your business handles temperature-sensitive items, you can explore further packaging best practices in our complete guide on packaging tips for cold food delivery.
For dependable temperature-controlled logistics solutions, visit our website at Hew Transportation to learn how we support safe, efficient, and compliant cold chain transport across Singapore.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
How do companies maintain stable temperatures during transport?
By using refrigerated vehicles, insulated packaging, and real-time temperature sensors that track conditions throughout the journey.
What happens if temperatures drop or rise outside the safe zone?
Deviations trigger alerts, allowing drivers or managers to take corrective action. Products may also undergo quality inspections upon arrival.
Is dry ice safe to use for frozen food delivery?
Yes. Dry ice is commonly used for frozen goods because it keeps items extremely cold without leaving residue.
How do you ensure food safety in last-mile delivery?
We rely on insulated carriers, fast drop-off procedures, and monitoring logs to maintain temperature stability.
Which industries require cold chain delivery?
Food and beverages, pharmaceuticals, chemicals, floral products, and biotechnology sectors all depend on temperature-controlled transport.